Nitric acid and Potassium hydroxide Reaction | HNO3 + KOH
Nitric acid (HNO3) reacts with Potassium hydroxide (KOH) gives potassium nitrate (KNO3) and water (H2O) as results. Heat is released due to neutralization of a strong acid (HNO3) and a strong base (KOH).
In this tutorial, we will discuss followings.
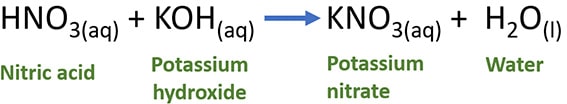
Balanced reaction of HNO3 and KOH
HNO3(aq) + KOH(aq) → KNO3(aq) + H2O(l)
One mole of HNO3 reacts with two moles of KOH. As products, one mole of KNO3 and two moles of H2O are given.
Reactants of reaction
Potassium hydroxide (KOH)
Potassium hydroxide is a white solid at room temperature and readily soluble in water. Aqueous Potassium hydroxide solution is a strong base because it completely dissociates to K+ and OH- ions in water. Due to strong basic characteristics, aqueous KOH should show pH values much higher than 7.
Nitric acid (HNO3)
Nitric acid is a strong acid because it completely dissociates to H+ and NO3- ions in water. These nitric acid solutions should show pH values much lower than 7 due to its strong acidic nature.
Products of reaction
Potassium nitrate (KNO3
Potassium nitrate is a salt and soluble in water to form a colourless aqueous solution.
Heat generation when HNO3 and KOH are neutralized
When one mole of water is generated due to neutralization of strong acid and strong base, -57.1kJ is released. Because one water mole is generated according to the above stoichiometric balanced equation, -57.1 kJ is released when HNO3 is neutralized by KOH.
Change of oxidation numbers
This reaction is not a redox reaction because oxidation numbers of atoms are not changed during the reaction.
- Potassium's only oxidation state is +1. In both KOH and KNO3, potassium is at +1 oxidation state.
- Nitrogen's oxidation number in HNO3 is +5. And also, on KNO3, oxidation number of nitrogen is +5.
Physical and chemical observation of HNO3 and KOH reaction
Here, we will see some physical observations and chemical properties changes during the reaction.
Colour and physical state changes
- Both aqueous HNO3 and aqueous KOH are colourless aqueous solutions.
- KNO3 which is given as a product is readily soluble in water and give a colourless aqueous solution.
pH change
- Reactants: KOH is a strong base and show pH value higher than 7 and HNO3 is strong acid and should show pH value less than 7.
- Products: KNO3 is a salt. Both K+ and NO3- ions are stable in water and do not participating in hydrolysis reactions. If all HNO3 and KOH are completely reacted with each other, pH of final solution should be 7.
Safety and health hazards possible of HNO3, KOH and KNO3
- HNO3: May intensify fire; oxidizer, severe skin burns (skin corrosion and irritation) and eye damage, Fatal if inhaled.
- KOH: Harmful if swallowed, severe skin burns (skin corrosion and irritation) and eye damage
- KNO3: May intensify fire; oxidizer, damage to organs
- Heat generation: Due to generation of large heat in a short time period, be careful to not touch beaker or other where reaction is being happened.
Questions
what happens when potassium hydroxide reacts with nitric acid
Reaction mixture and container will be heated due to the release of energy due to the neutralization process of acid and base. According to the mixed concentrations and volumes, generated heat quantity varies.