Oxidation of Primary, Secondary, Tertiary Alcohols to Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic Acid
Oxidation of primary, secondary, tertiary alcohols will give aldehyde, ketone and carboxylic acid as products. For oxidation, several oxidizing agents are used. According to the alcohol type, given product will vary.
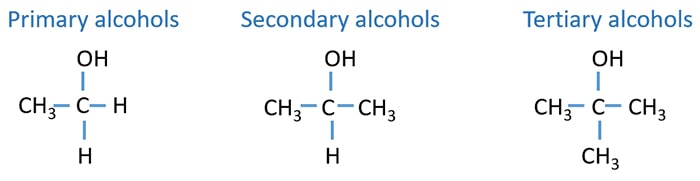
Primary, secondary, tertiary alcohols
According to the number of alkyl groups around the carbinol carbon, alcohols are categorized as primary, secondary, tertiary alcohols. According to the type of alcohol, they response in different way for oxidizing agents.
Primary alcohols
When there are no alkyl groups or one alkyl group around the carbinol carbon, those alcohols are defined as primary alcohol.
Secondary alcohols
When there are two alkyl group around the carbinol carbon, those alcohols are defined as primary alcohol.
Tertiary alcohols
When there are three alkyl group around the carbinol carbon, those alcohols are defined as primary alcohol.
Oxidizing agents
In alcohol oxidation, we use two types of oxidizing agents, strong and mild. Sometime, same alcohol will give different products for strong oxidizing agents and mild oxidizing agents.
Strong oxidizing agents
Following reagents are used as strong oxidizing agents in alcohol oxidation.
How do we know, alcohol is oxidized?
Strong oxidizing agents have colours. Colour of oxidizing agent is changed when alcohol is oxidized. You will learn more about these colour changes in next sections in this tutorial.
Strong oxidizing agents and their colour changes in alcohol oxidation
| Name | Chemical Formula | Description | Colour change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acidic potassium permanagante | H+ / KMnO4 | +7 oxidation state of manganese in KMnO4 is reduced to +2 Mn2+ ion. | Purple colour is changed to colourless or light pink. |
| Acidic potassium chromate | H+ / K2CrO4 | +6 oxidation state of chromium in K2CrO4 is reduced to +3 Cr3+ ion. | Yellow colour is changed to green. |
| Acidic potassium dichromate | H+ / K2Cr2O7 | +6 oxidation state of chromium in K2CrO4 is reduced to +3 Cr3+ ion. | Orange colour is changed to green. |
Mild oxidizing agents
Pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is used as the mild oxidation agent oxidation of primary alcohol to an aldehyde.
Alcohols oxidation
Now we are going to learn, which products are given by oxidation of different alcohol types.
| Alcohol type | Product given with Strong oxidizing agent | Product given with mild oxidizing agent |
|---|---|---|
| Primary alcohol | Carboxylic acid | Aldehyde |
| Secondary alcohol | Ketone | Ketone (Oxidation of secondary alcohol by mild oxidizing agent is rare) |
| Tertiary alcohol | No oxidation, No product | No oxidation, No product |
Primary alcohol oxidation
Primary alcohols can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and mild oxidizing agents.
Primary alcohols and strong oxidizing agents
Primary alcohol is oxidized to carboxylic acid by H+ / KMnO4 or H+ / K2CrO4 or H+ / K2Cr2O7.
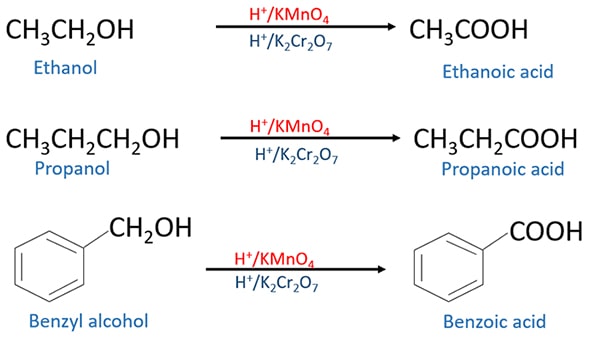
As an intermediate product, aldehyde is given. But aldehyde is again oxidized to carboxylic acid. So aldehyde cannot be separated. So we cannot produce an aldehyde from the reaction of primary alcohols and strong oxidizing agents.
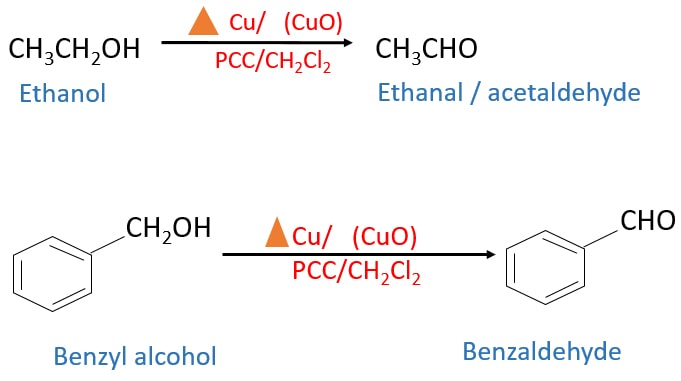
Primary alcohols and mild oxidizing agents
Primary alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde from PCC.
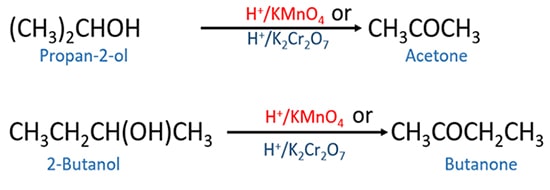
Secondary alcohol oxidation
Using any of strong oxidizing agents and mild oxidizing agents, secondary alcohols can be oxidized to ketones.
Most occasions, oxidation of secondary alcohol is done by strong oxidizing agent. Use of mild oxidizing agents is rare.
Tertiary alcohol oxidation
Due to no hydrogen atoms on the carbinol carbon in the tertiary alcohol, they are not oxidized.
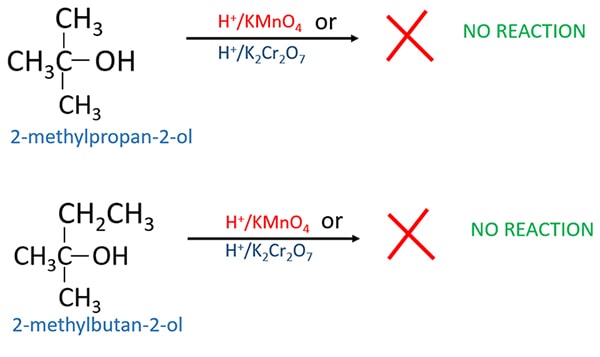
Identify alcohols from oxidation reactions
Now, we are going to learn how to identify primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols from strong oxidizing agent?
- Primary and secondary alcohols cannot be identified because both alcohol types are oxidized by strong oxidizing agents.
- Tertiary alcohols can be identified from Primary and secondary alcohols because tertiary alcohols are not oxidized by strong oxidizing agents.
Questions asked by students
alkene to alcohol to acid
Alkene is oxidized to alcohol by dilute sulfuric acid. According to the alkene structure, different type of alcohol is given. Then, alcohol is oxidized according to the requirement.
reagent (combinations) cannot be used to oxidise alcohols
Reagents which are used for oxidizing alcohols depend on thetype of alcohol. Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidized by oxidizing agents (like acidic potassium permanganate) which can oxidizde primary and secondary alcohols.
Oxidation of a tertiary alcohol will produce
Tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidized easily. So, we cannot expect a product from a such thing as oxidation of a tertiary alcohol
what are the products of oxidation of a primary alcohol?
Aldehyde or carboxylic acids are the products of oxidation of primary alcohol according to the added reagent.
Give the list of mild oxidizing agents which can oxidize primary alcohols to aldehyde
- PCC - Piridiniumchlorochromate
- Heated CuO
- Heated Ag2O
What will happen to the oxidation number of carbinol carbon atom of primary alcohols in the oxidation?
If primary alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde, oxidation number of carbon increases from -1 to +1.
If primary alcohol is oxidized to an carboxylic acid, oxidation number of carbon increases from -1 to +3.
What is the difference of primary alcohol oxidation and alkene oxidation by a strong oxidizing agent in acidic medium?
In alkenes, double bond is broken in the oxidation process. But according to the location of double bond, produced products are different. But, when primary alcohols are oxidized by a strong oxidizng agent in acidic medium, carboxylic acid is given always.
primary alcohol to ketone?
You cannot convert every primary alcohols such as ethanol, methanol to ketone because there is not enough carbon groups to exist around carbonyl group.
But, when you have a primary alcohol such as propanol, you can convert it to propanone (ketone with three carbon atoms). But, this reaction is not a single step reaction and have to do several reactions.
- Propanol to propene
- Propene to 2-propanol
- 2-propanol to propanone
How to identify oxidation of primary alcohols?
When primary alcohols are oxidized, colour of oxidizing agent is changed due to reduction of oxidizing agent.
can tertiary alcohols be oxidized?
Under conditions of oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols, tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidized.
What is the difference between alcohol oxidation and alkene oxidation by strong oxidizing agents in acidic medium?
Alkene oxidation may give carboxylic acids or ketones or both of them as products. But in alkenes, double bond is broken (carbon chain is broken). But in alcohols, carbon chain is not broken.
What are the oxidation numbers of reagent used in oxidation of primary alcohol to carboxylic acid
In acidic potassium permanagante, manganeese is at +1 oxidation state. In potassium dichromate and potassium chromate, chromium is at +6 oxidation state.
I cannot see the colour change of acidic potassium permanganate when ethanol is oxidized? What are the reasons for it?
If you use excess acidic potassium permanganate (higher concentration), we are unable to see the colour difference because some potassium permanganate is still there in the solution and give purple colour.
Can I identify ethanol and propanol from oxidation?
Both ethanol and propanol are primary alcohols and answers in similar way in oxidation reactions. So we cannot see a difference and could not identify ethanol and propanol.
oxidation of propanol, is that secondary alcohol oxidation?
Propanol is an primary alcohol and it can be oxidized to propanoic acid or propanal by strong oxidizing agent and mild oxidizing agent respectively.
Can a primary alcohol be oxidized to a ketone?
Like compounds methanol, ethanol cannot be oxidized to ketone because they have less than two carbon atoms. For a ketone, at least three carbon atoms are required. So, when an primary alcohol has three or more carbon atoms, there is possibility to produce a ketone by several steps (reactions).
which type of alcohol is most easily oxidized?
Primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidized easily.
If you cannot identify, primary alcohol and secondary alcohol from oxidation, how it is possible to identify them?
Lucas' reagent can be used to identify primary and secondary alcohol.
What are the differences of oxidation of aldehydes and primary alcohols by strong oxidizing agents?
Both aldehyde and alcohols can be oxidized easily to carboxylic acids. The amount required for oxidation of aldehyde is less than amount required for alcohol because aldehyde is much oxidized than alcohols.
Can you prepare propanone by oxidation propanol?
You cannot do this in a single reaction. But by several steps of reactions, you can prepare propanone by propanol. Preparing propanone, 2-propanol is oxidized.
What will happen if an alcohol with an double bond between two carbon atom (alkene) is oxidized?
The molecule is broken across the double bond and oxidized as several groups. The alcohol group is oxidized as learnt. But molecule is not same as before.
Cannot primary alcohols be oxidized to carboxylic acid by concentrated sulfuric acid alone?
No. primary alcohols cannot be oxidized to carboxylic acid by concentrated sulfuric acid because oxidizing power of concentrated sulfuric acid is not enough. But when concentrated sulfuric acid is heated with alcohols, as products alkenes are given.
oxidation of secondary alcohol to carboxylic acid
Secondary alcohol cannot be oxidized to a carboxylic acid in one step. You have to convert secondary alcohol to primary alcohol and then oxidize it to a carboxylic acid compound. As an example, converting 2-propanol to propanol can be shown.
conditions from secondary alcohol to carboxylic acid
You can convert a secondary alcohol to carboxylic acid from two methods. One is increasing number of carbon atoms or producing a primary alcohol.Second methods is limited to very few secondary alcohols because it is difficulat to convert a secondary alcohol to a primary alcohol.
In the second method, you can convert secondary alcohol to an alkyl halide compound. Then secondary alcohol is treated with aqueous alcoholic KCN. Then given product is treated with dilute sulfuric acid to produce carboxylic acid.
whats the difference between ketones and carboxylic acids in oxidations of alcohols
In carboxylic acid molecule, oxidized carbon atom show a higher oxidation number than the oxidized carbon atom in ketone.
When primary alcohols are oxidized by a strong oxidizing agent, carboxylic acid is given. To get a ketone, you have to oxidize a secondary alcohol. For secondary alcohol oxidation, you can use strong oxidizing agent or mild oxidizing agent.
You know oxidation of alcohols can be used to identify alcohols. Can it be used to identify an alkene with different isomers?
Alkens are oxidized by strong oxidizing agent such as acidic potassium permanganate. But carbon chain is broken acrosss the double bond in the oxidation process and as products carboxylic acids, ketones or carbon dioxide can be given.
where we use PCC as an oxidising agent?
PCC is used in primary alcohol oxidation to aldehyde.
CH203_204_Lab_Manual Oxidation a Secondary Alcohol
Secondory alcohols are oxidized to ketones by strong oxidizing agents and mild oxidizing agents.
oxidation of alcohols to aldehyde vs carboxylic acids
According to the used oxidizing agent, aldehyde or carboxylic acid is given as the product of alcohol oxidation.
colour change of oxidising alcohols to make carboxylic acid
If alcohols are oxidized to carboxylic acids by strong oxidizing agents, their color changes like below.
- Purple colour of acidic potassium permanganate is changed to pale pink colour or become colourless.
- Orange colour of acidic potassium dichromate is changed to green colour.
- Yellow colour of acidic potassium dichromate is changed to green colour.